 Inversion adalah sebuah nama untuk pembalikan pola suatu kalimat dalam Bahasa Inggris, dimana subjek dan predikat berada dalam posisi yang berbeda dari posisi semula. Pada umumnya inversion ini digunakan dalam kalimat pernyataan dan pertanyaan. Di dalam bahasa Inggris, subjek dan kata kerja terkadang dibalik jika berada setelah kata pernyataan tempat, seperti here, there, atau nowhere. Subjek dan kata kerja juga bisa dibalik setelah pernyataan negative dan berkaitan. Ketika pernyataan negative, seperti no, not, atau never, berada di awal kalimat, subjek dan kata kerjanya dibalik. Dalam soal TOEFL Structure and Written Expression, Anda bisa saja menemukan soal bentuk inversion (susun balik) ini. Perhatikan bentuk-bentuk inversion berikut ini.
Inversion adalah sebuah nama untuk pembalikan pola suatu kalimat dalam Bahasa Inggris, dimana subjek dan predikat berada dalam posisi yang berbeda dari posisi semula. Pada umumnya inversion ini digunakan dalam kalimat pernyataan dan pertanyaan. Di dalam bahasa Inggris, subjek dan kata kerja terkadang dibalik jika berada setelah kata pernyataan tempat, seperti here, there, atau nowhere. Subjek dan kata kerja juga bisa dibalik setelah pernyataan negative dan berkaitan. Ketika pernyataan negative, seperti no, not, atau never, berada di awal kalimat, subjek dan kata kerjanya dibalik. Dalam soal TOEFL Structure and Written Expression, Anda bisa saja menemukan soal bentuk inversion (susun balik) ini. Perhatikan bentuk-bentuk inversion berikut ini.
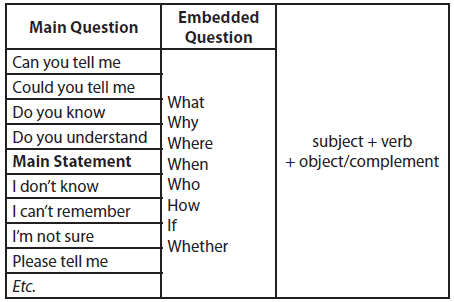
1. Embedded Question
Embedded Question adalah sebuah pertanyaan yang berada di dalam pertanyaan atau pernyataan lain. Embedded Question ini memiliki efek yang tidak begitu terlihat.
Contoh:
Simple Question : Who is he? (He is my father/He is my friend)
Simple Statement : I don't know him.
Embedded Question dalam question : Do you know who he is? (Yes, I do/No, I don't.)
Embedded Question dalam pernyataan: I don't know who he is.
Lebih jelasnya, penggunaan Embedded Question dapat dilihat pada tabel berikut:
Contoh:
Embedded Question dalam pertanyaan:
- Do you know what the housing market will be like next year?
- Can you tell me how I can arrive there?
- Do you know what time it is?
Embedded Question dalam pernyataan:
- I don't know how I'll be able to retire at 65. It's so hard to save money nowadays!
- I can't remember why I decided to get an MBA.
- He's not sure if he can fly in for the wedding next month.
Susah cari metode belajar TOEFL yang Efektif?... Susah cari downloadannya?
Sudah kami sediakan superlengkap!
2. Negative
Either digunakan setelah kata kerja negatif. Contoh:
a) I'm not happy. (Saya tidak bahagia.)
→ I'm not happy either. (Saya juga tidak bahagia.)
b) I can't help you. (Saya tidak bisa membantumu.)
→ I can't help you either. (Saya juga tidak bisa memban-tumu.)
c) George doesn't watch TV. He doesn't study either. (George tidak menonton TV. Dia juga tidak belajar.)
Neither penanda negatif yang berasal dari not + either. Neither digunakan di bagian awal sebelum kata kerja dan subjek. Contoh:
a) I haven't got an answer.
→ Neither have I. (= I haven't either.)
b) I can't cook.
→ Neither can I. (I can't either.)
c) I never go to Paris.
→ Neither do I (I don't either.)
Neither dapat diganti dengan nor.
Contoh:
a) I haven't got an answer. → Nor have I.
b) I can't cook. → Nor can I.
c) I never go to Paris. → Nor do I.
3. Conditional Sentence
Conditional 1 (Real Conditional Sentence, Possibility) Bentuk kalimat pada bagian ini menyajikan situasi yang nyata atau mungkin terjadi. Contoh:
- He will arrive late unless he hurries up.
- Jenny will buy a new bike if she gets her raise.
- If it rains, I will stay at home.
Conditional 1 atau possibility dibentuk oleh penggunaan bentuk present simple di dalam klausa if. Jika klausa if muncul di awal maka tidak diperlukan tanda koma, namun jika klausa if muncul di akhir setelah present simple maka diperlukan tanda koma.
Contoh:
Menggunakan tanda koma (,)
- If she finishes on time, she will go to the cinema.
- If he asks me, I will help him.
- If Grace invites him, he will attend the party.
Tanpa menggunakan tanda koma (,)
- She will go to the cinema if she finishes on time.
- I will help him if he asks me.
- He will attend the party if Grace invites him.
Conditional 2 (Present Unreal Conditional Sentence)
Present unreal conditional digunakan untuk mengekspresikan kondisi saat ini. Kalimat ini disebut unreal (tidak nyata) karena kalimat ini menyampaikan kepada kita apa yang akan terjadi atau bagaimana sesuatu itu ada, seandainya situasinya berbeda.
Contoh:
- If I had a car, I would visit you often. (= I don't have a car. I don't visit you often.)
- If they weren't so expensive, I would have one. (= They are so expensive. I don't have one.)
- If you didn't work so hard, you wouldn't be tired all the time. (= You work so hard. You are tired all the time.)
Note: Pada bentuk ini seluruh subjek orang menggunakan ‘were' untuk menggantikan ‘to be'. Contoh:
- If I were you, I would be more careful.
- If you were leaving earlier, I would go with you.
- I would lower taxes if I were the President.
Conditional 3 (Past Unreal Conditional Sentence)
Past Unreal Conditional Sentence terdiri atas dua klausa, yaitu if clause dan would clause.
If clause mengacu pada sebuah kondisi atau peristiwa lam-pau yang tidak nyata.
Contoh:
- If I had finished the test, ...
- If it hadn't rained lastnight, ...
- If I had arrived there, ...
Would clause merupakan konsekuensi atau akibat dari if clause.
Contoh:
- I would have got a highscore.
- We would have gone to the party.
- It wouldn't have been fun.
Bentuk inversi pada conditional sentence:
Conditional sentence tipe II dengan if clause mengandung to be ‘were' dan conditional sentence tipe III bisa disusun dengan bentuk susun balik atau inversi dengan pola se-perti di bawah ini:
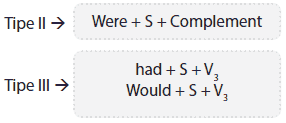
Contoh:
- If I were a richman, I could help your financial problem → were I a richman, I could help your financial problem.
- If I had joined the contest, I would have become a famous singer → had I joined the contest, I would have become a famous singer.
